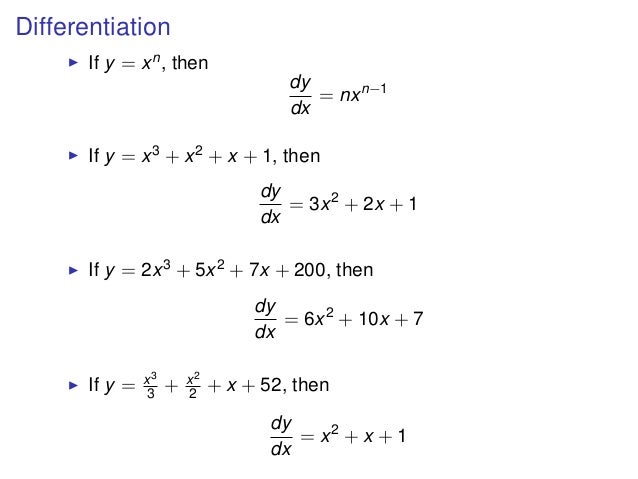
D Dx Formula
Answer to Find the general solution of the differential equation (x 2y 1) dx (2x 4 y) dy = 0 By signing up, you'll get thousands of1 Substitute y = uv, and dy dx = u dv dx v du dx into dy dx P(x)y = Q(x) 2 Factor the parts involving v;
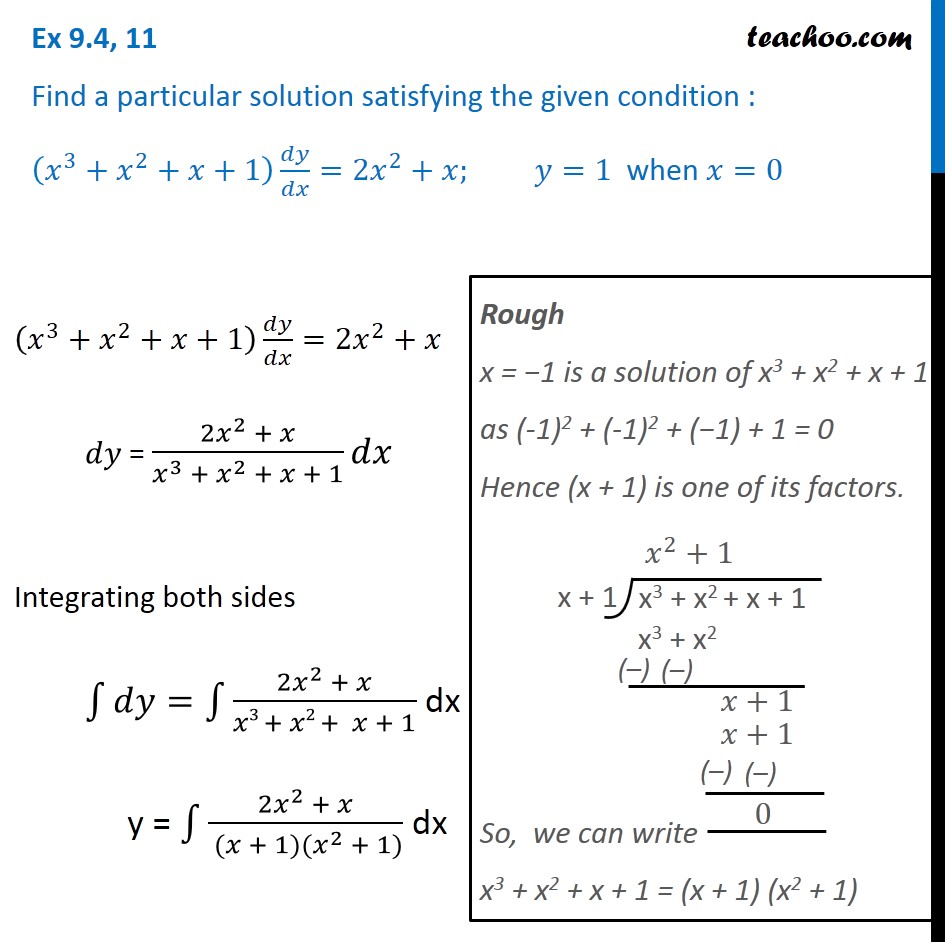
X 3 x 2 x 1 dy / dx 2x 2 x y 1 when x 0
X 3 x 2 x 1 dy / dx 2x 2 x y 1 when x 0-Dydx = 2xy1x 2 Step 1 Separate the variables Multiply both sides by dx, divide both sides by y 1y dy = 2x1x 2 dx Step 2 Integrate both sides of the equation separately ∫ 1y dy = ∫ 2x1x 2 dx The left side is a simple logarithm, the right side can be integrated using substitutionEjercicios EDO's de primer orden 3 1 y3 dy = dx x2 Z y−3 dy = Z x−2 dx, 1 −2 y−2 = −x−1 c 1, −1 2y2 −1 x c 1, 1 y2 2 x c, c = −2c 1 Solución implícita 1 y2 2xc x Solución explícita y = ±

Solve Y 2 2x 2y Dx 2x 3 Xy Dy 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange
If 2x = y1/3 y–1/3, prove that (x2 – 1)(d2y/dx2) x (dy/dx) – 9y = 0 Welcome to Sarthaks eConnect A unique platform where students can interact with teachers/experts/students to get solutions to their queries\frac{dy}{dx}=1x^2y^2, Given Here, \frac{dy}{dx} represents the derivative of y with respect to x I will solve for x and y, treating y as a function of x (essentially y=f(x)) \int \frac{dy}{dx}dx=\int 1x^2y^2dxFree separable differential equations calculator solve separable differential equations stepbystep
If d 2 y/dx 2 = 0, you must test the values of dy/dx either side of the stationary point, as before in the stationary points section Example Find the stationary points on the curve y = x 3 27x and determine the nature of the points At stationary points, dy/dx = 0 dy/dx = 3x 2 27 If this is equal to zero, 3x 2 27 = 0 Hence x 2 9 = 0 (dividing by 3) So (x 3)(x 3) = 0Let's simplify it First dy/dx = (y/x 1)/(y/x 1) Taking y = vx dy/dx = v xdv/dx Therefore, dx/x = (v 1)dv / (v^2 1) Integrating we get log (1/x) logc = arctan (y/x) 1/2 logCalculus Find dy/dx y=1/x y = 1 x y = 1 x Differentiate both sides of the equation d dx (y) = d dx ( 1 x) d d x ( y) = d d x ( 1 x) The derivative of y y with respect to x x is y' y ′ y' y ′ Differentiate the right side of the equation Tap for more steps
X 3 x 2 x 1 dy / dx 2x 2 x y 1 when x 0のギャラリー
各画像をクリックすると、ダウンロードまたは拡大表示できます
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  |  |
「X 3 x 2 x 1 dy / dx 2x 2 x y 1 when x 0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  | |
 |  | |
「X 3 x 2 x 1 dy / dx 2x 2 x y 1 when x 0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  | |
 |  |  |
「X 3 x 2 x 1 dy / dx 2x 2 x y 1 when x 0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 | ||
 |  |  |
「X 3 x 2 x 1 dy / dx 2x 2 x y 1 when x 0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「X 3 x 2 x 1 dy / dx 2x 2 x y 1 when x 0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「X 3 x 2 x 1 dy / dx 2x 2 x y 1 when x 0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  | |
 |  |  |
「X 3 x 2 x 1 dy / dx 2x 2 x y 1 when x 0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 | ||
 |  | |
「X 3 x 2 x 1 dy / dx 2x 2 x y 1 when x 0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 | ||
 |  |  |
「X 3 x 2 x 1 dy / dx 2x 2 x y 1 when x 0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 | ||
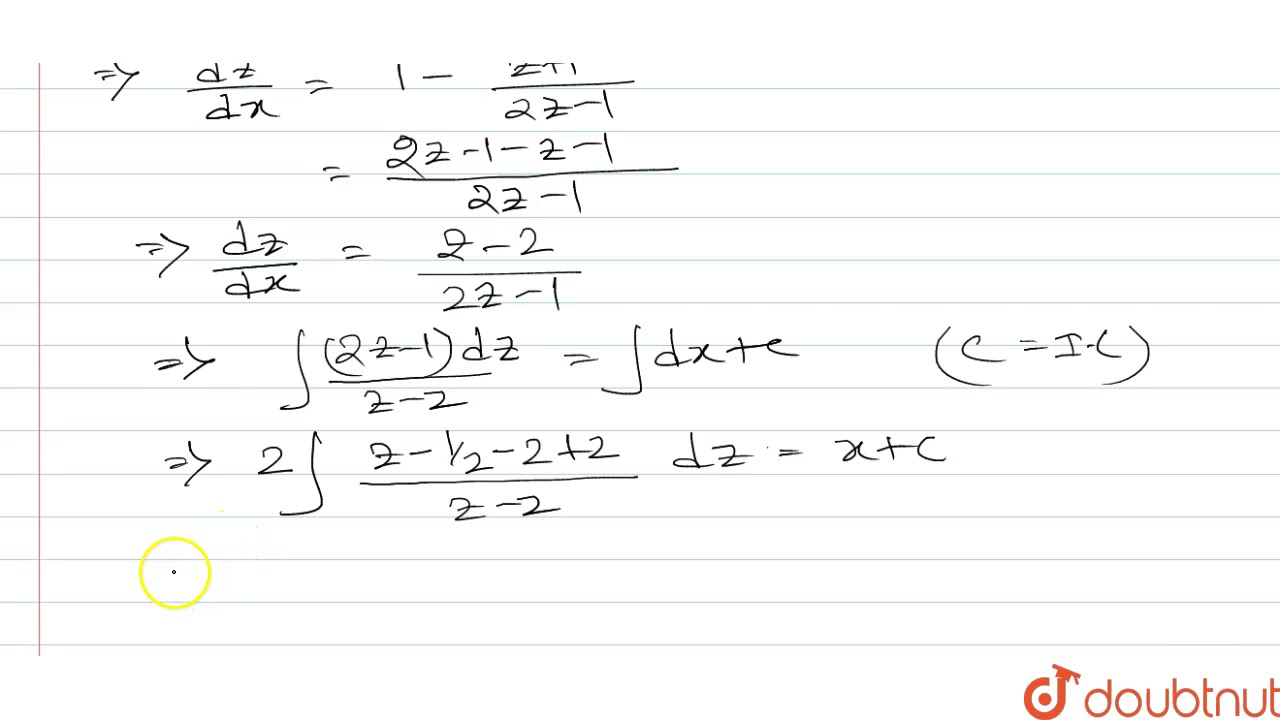 | ||
「X 3 x 2 x 1 dy / dx 2x 2 x y 1 when x 0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「X 3 x 2 x 1 dy / dx 2x 2 x y 1 when x 0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |
For x ≥ 3, any other distribution leaves either one of ( y − 1), ( y 1) to be odd or both of them a multiple of 4 In other words, it means either y − 1 = 2 x − 1 k or y 1 = 2 x − 1 k for some odd k (Note k is odd because 2 x − 1 should already account for all the powers of 2 which divide y ± 1 )Start with y = sin−1 (x) In non−inverse mode x = sin (y) Derivative d dx (x) = d dx sin (y) 1 = cos (y) dy dx Put dy dx on left dy dx = 1 cos (y) We can also go one step further using the Pythagorean identity sin 2 y cos 2 y = 1 cos y = √ (1 − sin 2 y ) And, because sin (y) = x (from above!), we get
Incoming Term: x 3 x 2 x 1 dy / dx 2x 2 x y 1 when x 0,




0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿